 The Appellate Division, Second Department, has again told J.H.O. Stanley Gartenstein that it was improper for him to award nontaxable spousal maintenance.
The Appellate Division, Second Department, has again told J.H.O. Stanley Gartenstein that it was improper for him to award nontaxable spousal maintenance.
In Siskind v. Siskind, in addition to awarding the wife $65,000 per year in nontaxable maintenance until the wife reached her 65th birthday, J.H.O. Gartenstein equitably distributed the parties’ assets, awarded child support and a $340,000 counsel fee, and secured the husband’s support obligations with a $4 million life insurance policy (reduced on appeal to $3 million).
In its November, 2011 modification of that award, the Second Department recognized the presumption that spousal maintenance should be taxable income to the recipient spouse, and deductible to the payor. The appellate court stated:
. . . there was insufficient evidence justifying the Supreme Court’s direction that maintenance be nontaxable to the plaintiff, which is “a departure from the norm envisioned by current Internal Revenue Code provisions.”
In 2007, in Grumet v. Grumet, the Second Department had modified J.H.O. Gartenstein’s award to the wife of non-taxable maintenance, declaring that in the absence of a stated rationale for a departure from the norm envisioned by the Internal Revenue Code provisions, a maintenance award should be taxable.
Maintenance is appropriately taxable income to the recipient. Baron v. Baron (2nd Dept. 2010), Markopulous v. Markopulos, 274 A.D.2d 457, 710 N.Y.S.2d 636 (2nd Dept. 2000) ; see also Taverna v. Taverna (2008), where the Second Department modified the trial court award by making maintenance taxable. Such may have been the holding because the trial court properly declined to consider the husband’s tax liabilities resulting from the liquidation and distribution of investment accounts incident to equitable distribution, as the husband had failed to offer any competent evidence concerning the liabilities which would be incurred. See Fleishmann v. Fleischmann (2010 Supreme Westchester Co., Lubell, J.)Continue Reading The Taxability of Spousal Maintenance Payments: a Subject of Inconsistent Court Decisions
 On October 25, 2011 the New York State Law Revision Commission held a round-table discussion to review New York’s spousal support, i.e. “maintenance” statute, Domestic Relations Law §236(B)(5-a, 6). The discussion precedes a final report which that Commission is required to render under a mandate imposed by the Legislature when new laws concerning temporary maintenance, interim counsel fees and no-fault divorce were adopted last year. In part, the Commission was charged to:
On October 25, 2011 the New York State Law Revision Commission held a round-table discussion to review New York’s spousal support, i.e. “maintenance” statute, Domestic Relations Law §236(B)(5-a, 6). The discussion precedes a final report which that Commission is required to render under a mandate imposed by the Legislature when new laws concerning temporary maintenance, interim counsel fees and no-fault divorce were adopted last year. In part, the Commission was charged to: Last week, the Appellate Division, Third Department, exercised its equitable muscle to filling in the gaps while the marriage and divorce laws of the different states catch up with each other. On July 21, 2011, in
Last week, the Appellate Division, Third Department, exercised its equitable muscle to filling in the gaps while the marriage and divorce laws of the different states catch up with each other. On July 21, 2011, in  The May, 2011 decision of the Appellate Division, Second Department, in
The May, 2011 decision of the Appellate Division, Second Department, in 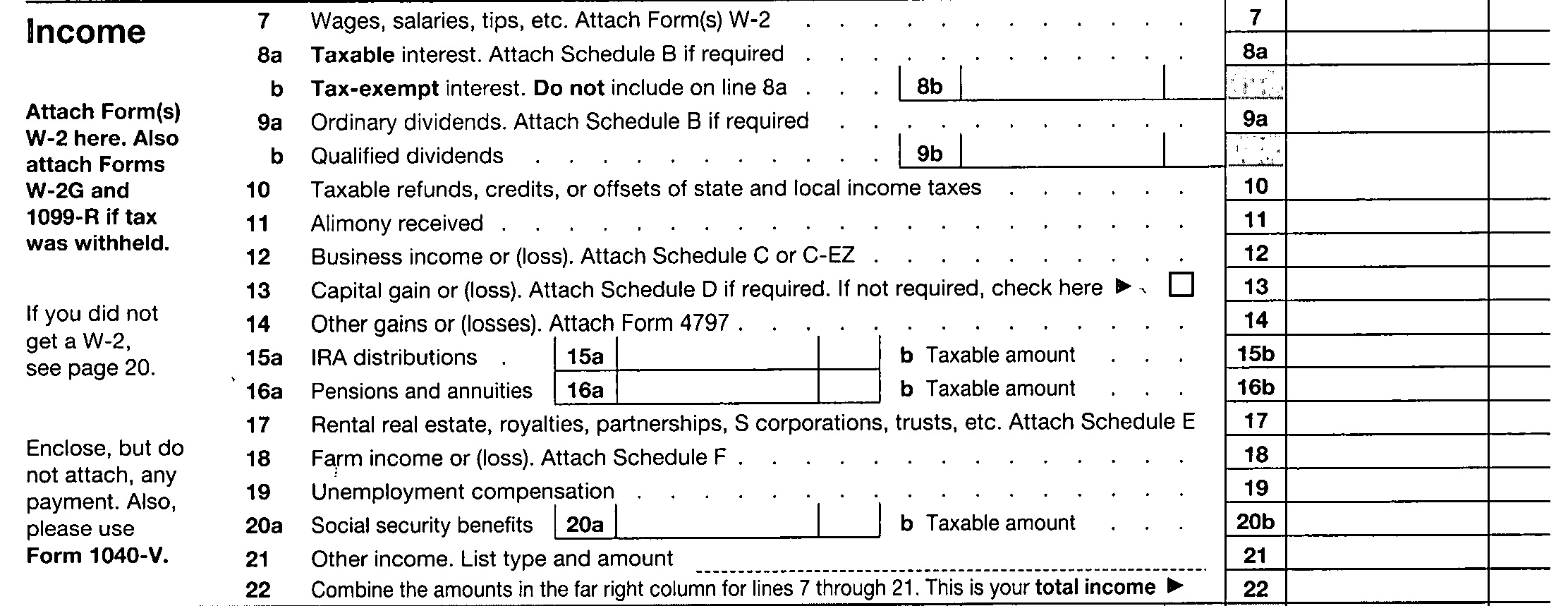
 In this second of two blogs discussing Supreme Court Nassau County Justice
In this second of two blogs discussing Supreme Court Nassau County Justice 

 With the addition on August 13, 2010 of D.R.L. §170(7), making New York the 50th state to grant no-fault divorces, Governor Patterson also signed an amendment to D.R.L. §237. That amendment creates a rebuttable presumption that while a divorce action is pending, the “less monied” spouse shall be awarded counsel and expert fees and expenses
With the addition on August 13, 2010 of D.R.L. §170(7), making New York the 50th state to grant no-fault divorces, Governor Patterson also signed an amendment to D.R.L. §237. That amendment creates a rebuttable presumption that while a divorce action is pending, the “less monied” spouse shall be awarded counsel and expert fees and expenses